✎ Andrés Rodriguez

✎ Diego Aguilera

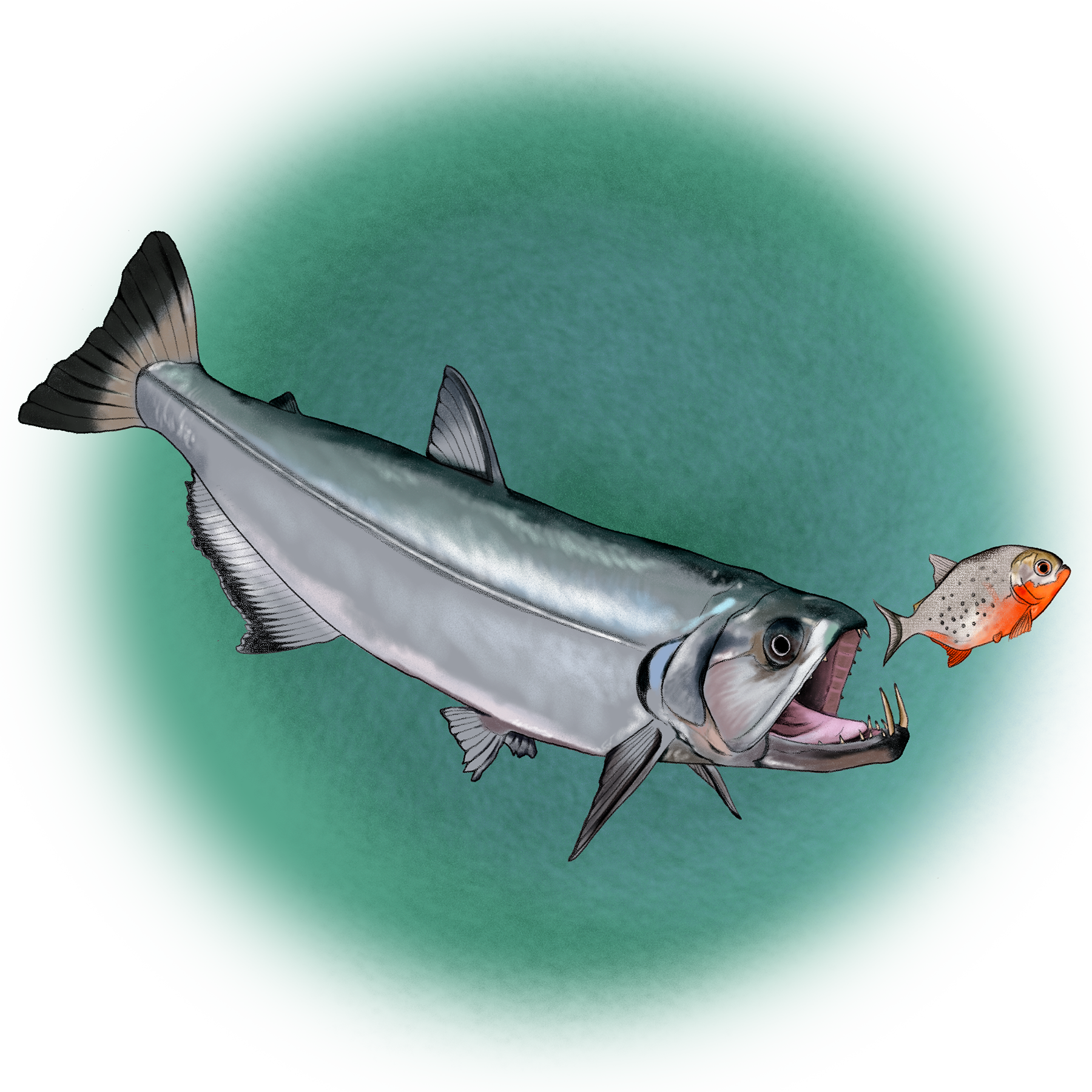
Vampire Tetra
Hydrolycus scomberoidesAmazon region
RECORRIDO VIRTUAL POR LA BIODIVERSIDAD DE COLOMBIA
Museo de Historia Natural
Universidad Nacional de Colombia

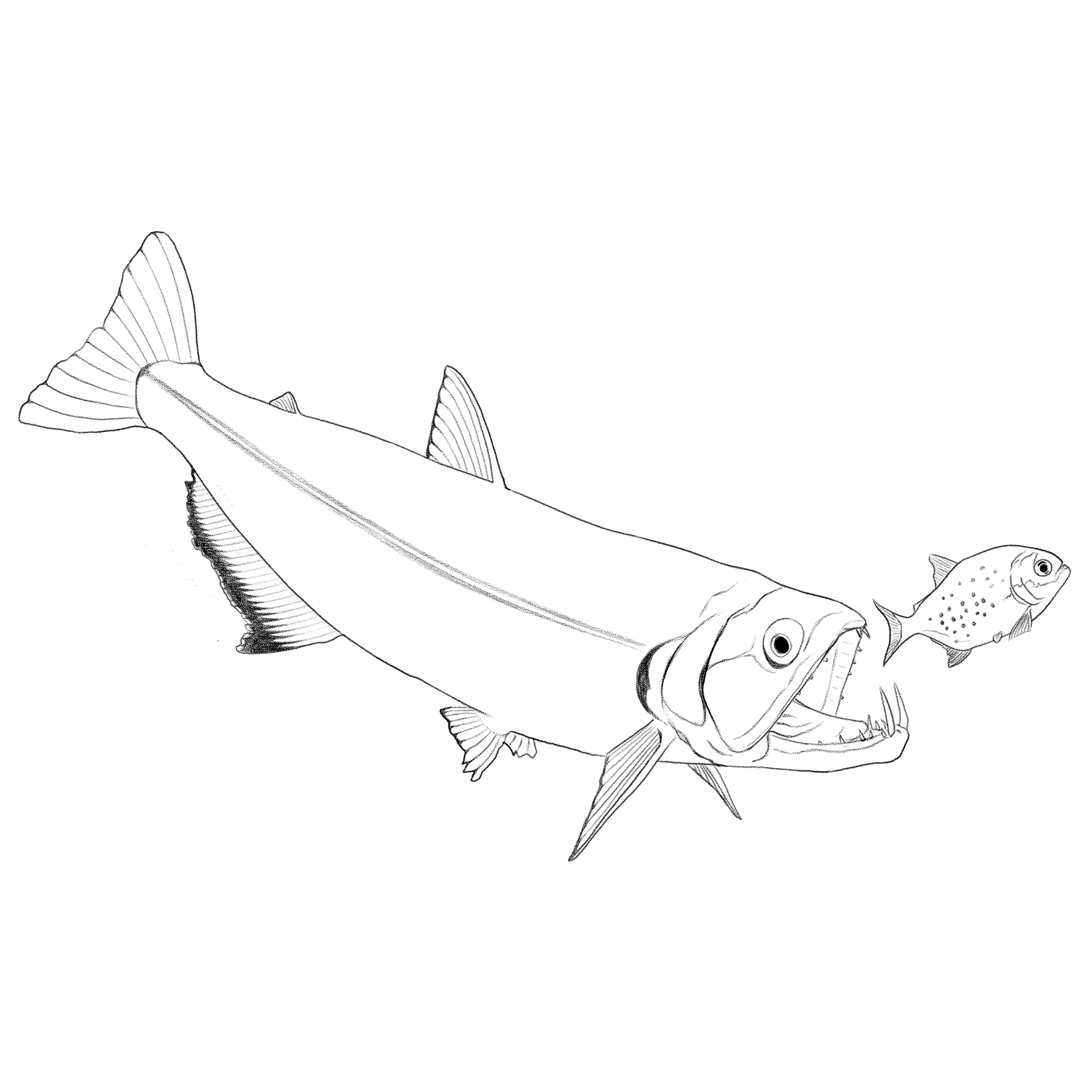
Vampire Tetra
Hydrolycus scomberoides
Morpho-functionality
Teeth
Its huge lower teeth help it capture and pierce its prey.
Tail
Its tail works like a powerful paddle when swimming quickly.
Tact
Like many other fish, it has a lateral line, which is an organ that helps it perceive the movement and vibrations of the water around it.
Lifecycle
Like many other fish, H. scomberoides reproduces during the flood period of rivers (between July and September), where the females release about 2,000 to 3,500 eggs. Egg laying is made close to the riverbanks. Together with other species of fish, it performs local and medium migrations of between 100 to 500 km distance.
Vampire Tetra
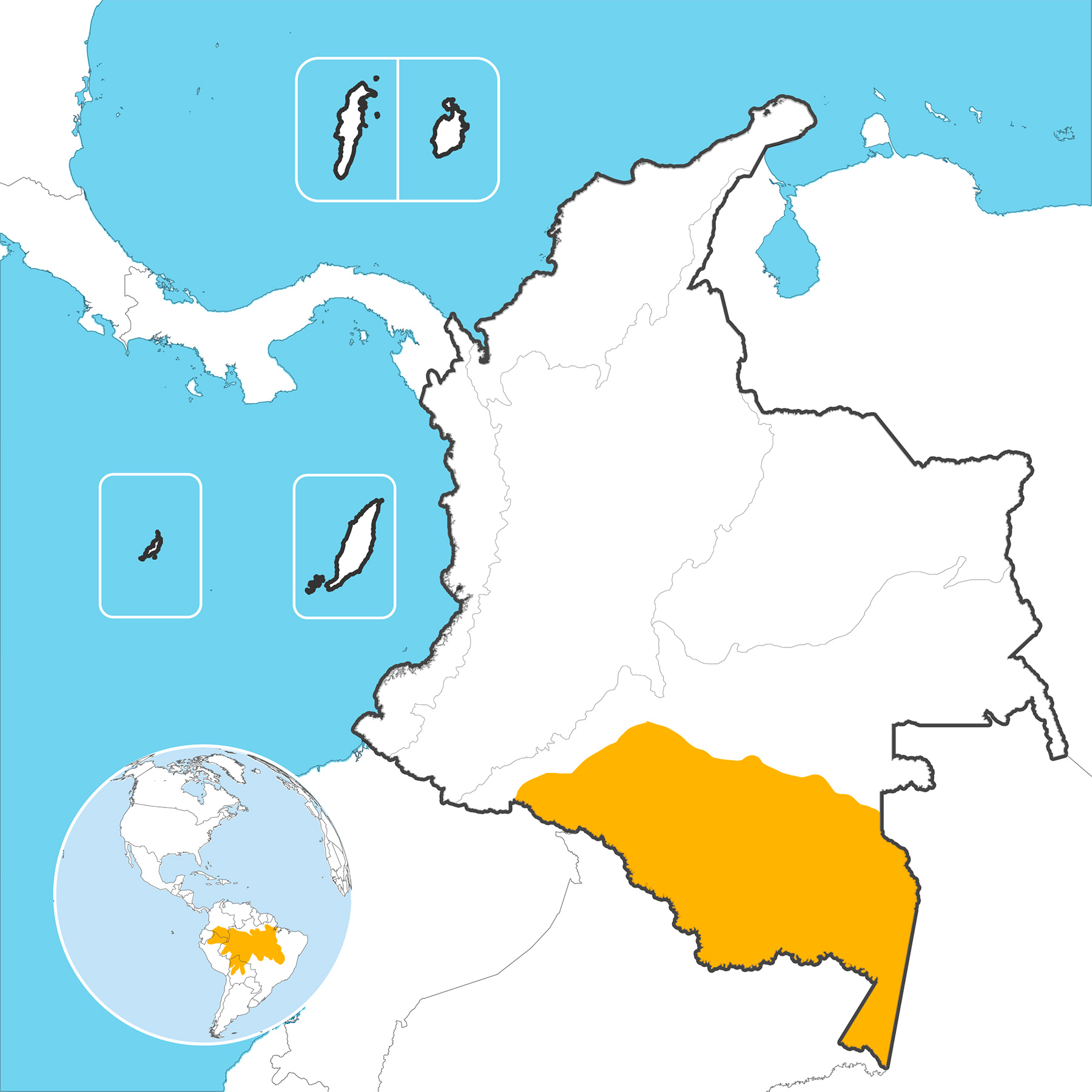
Distribution
It is a freshwater fish that inhabits the area of the bed and the water column of rivers, lakes and flooded forests of the Amazon basin and is distributed in Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela. Adults and juveniles are piscivorous while larvae feed on plankton. It tolerates temperatures between 24 and 28 ° C.
Distribution area