✎ Camila Espinosa

✎ Diego Aguilera

Golden Poison Frog
Phyllobates terribilisPacific region
RECORRIDO VIRTUAL POR LA BIODIVERSIDAD DE COLOMBIA
Museo de Historia Natural
Universidad Nacional de Colombia

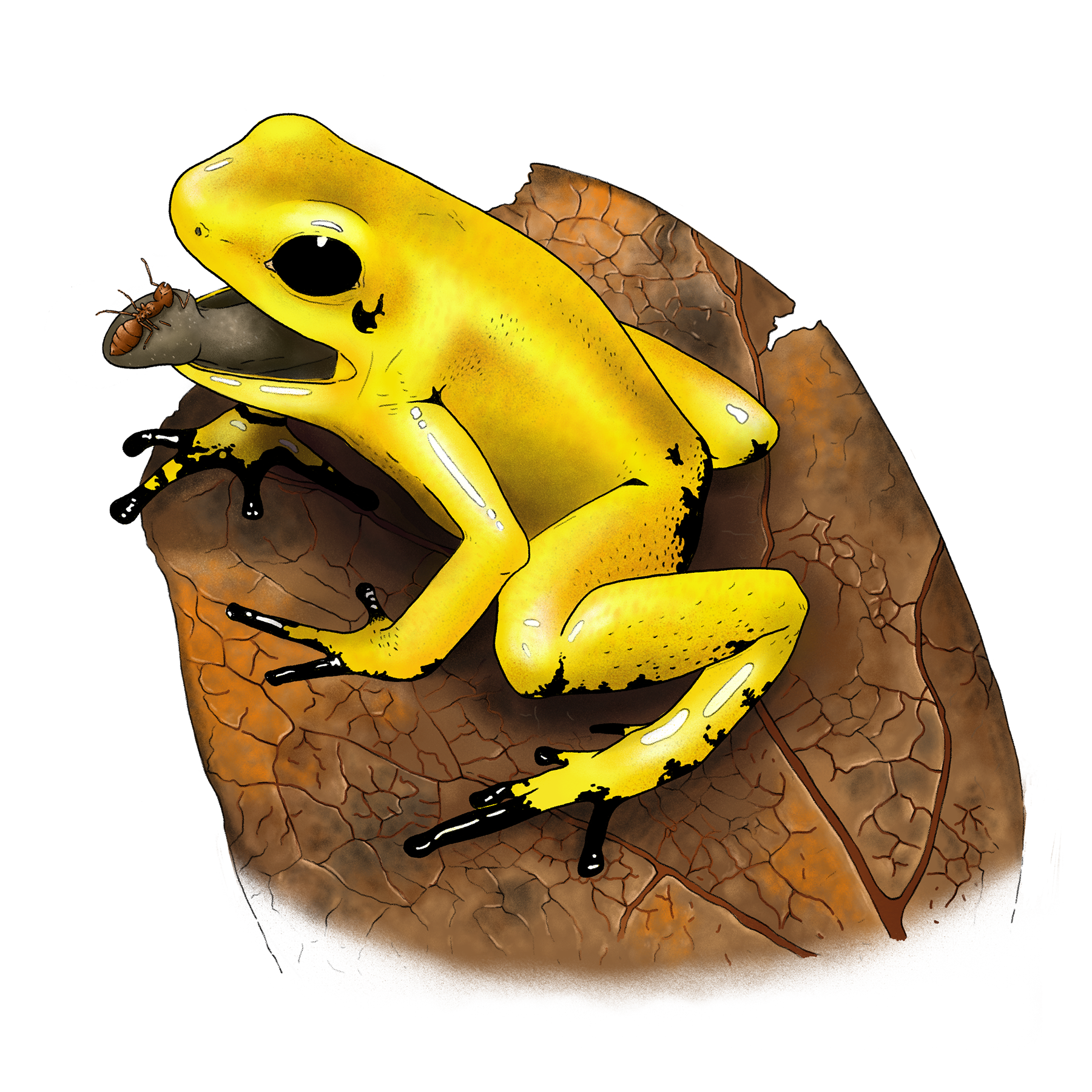
Golden Poison Frog
Phyllobates terribilis
Morpho-functionality
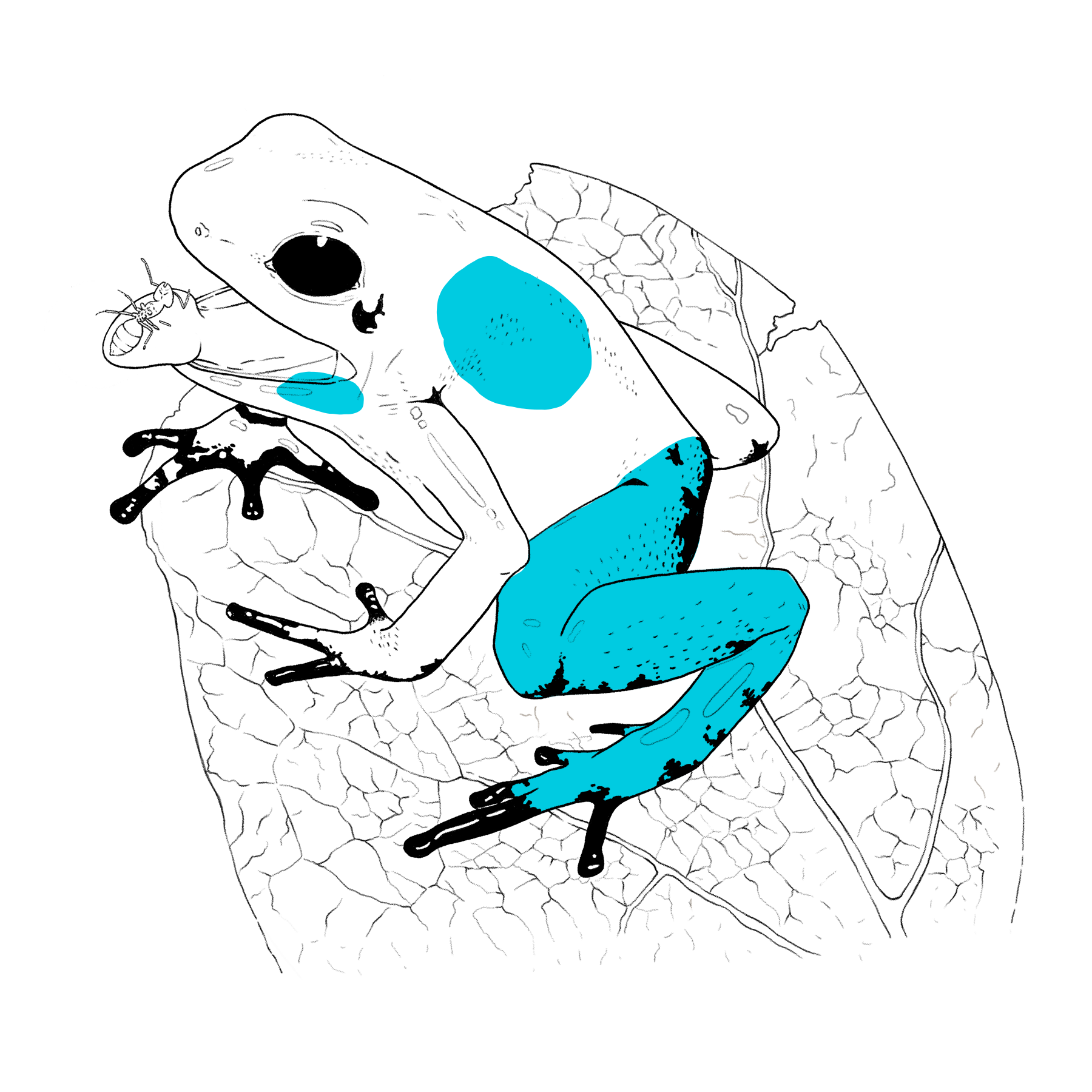
Skin
The coloration of this species of frog is aposematic, which means that it serves as a warning of the chemical defense mechanism that it has against predators.
Vocal sacs
Males have indentations or vocal sacs under the jaw, which they inflate and use to sing, woo females, and defend their territory.
Breathing
Despite having lungs, they also breathe through the skin through gas exchange.
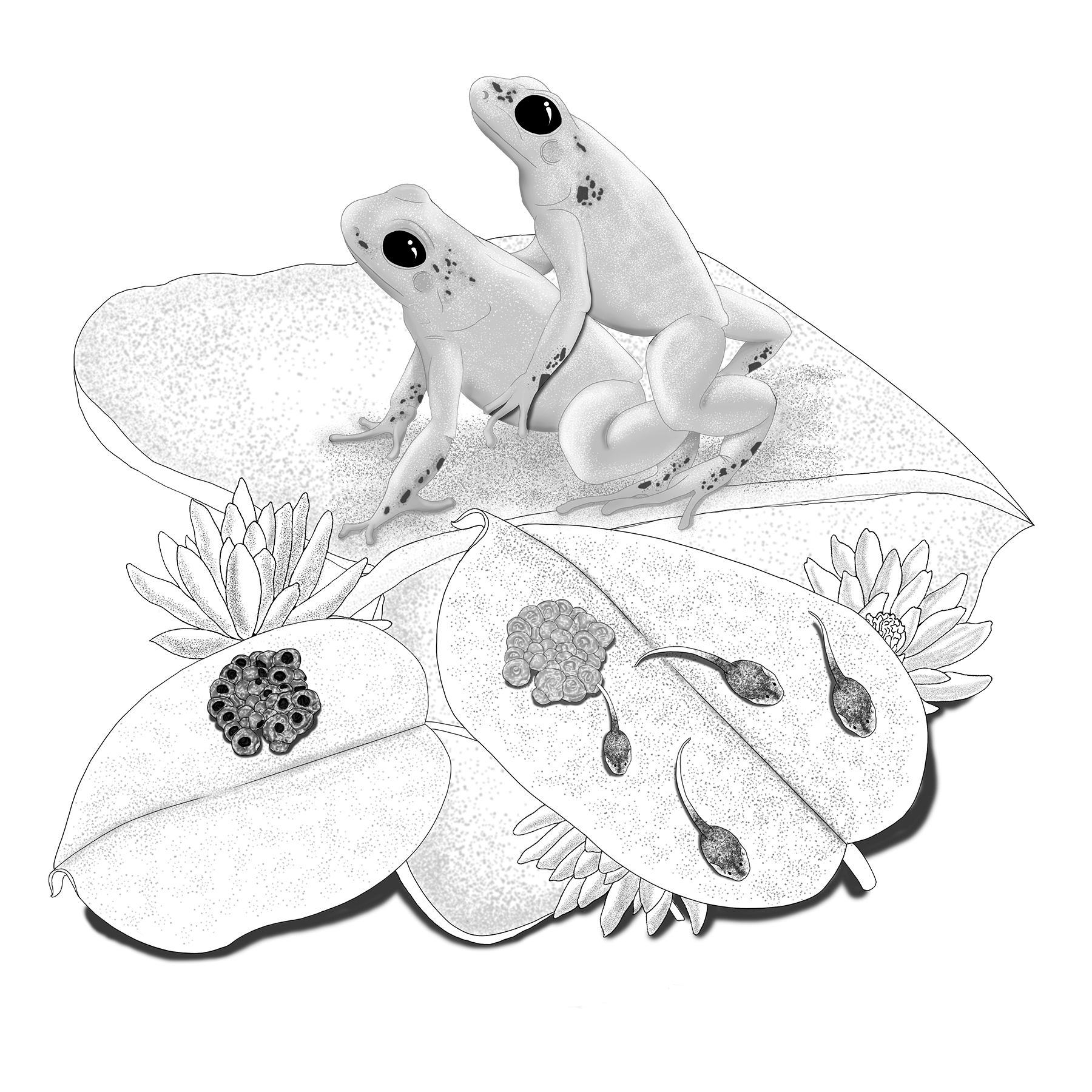
Lifecycle
During the reproductive season, males sing to attract females and to maintain their territory, after attracting them, a courtship is presented that includes visual, auditory and tactile signals. At the end of the courtship, the female deposits the eggs in the litter and the male fertilizes them by apposition of cloacas (approximation of the cloaca of the female and the male). It lays between eight to fifteen eggs, these hatch in two weeks and when they reach the 25th stage of development they are transported by the male to bodies of water, they finish their metamorphosis after two months and their sexual maturity is reached one year.
Golden Poison Frog
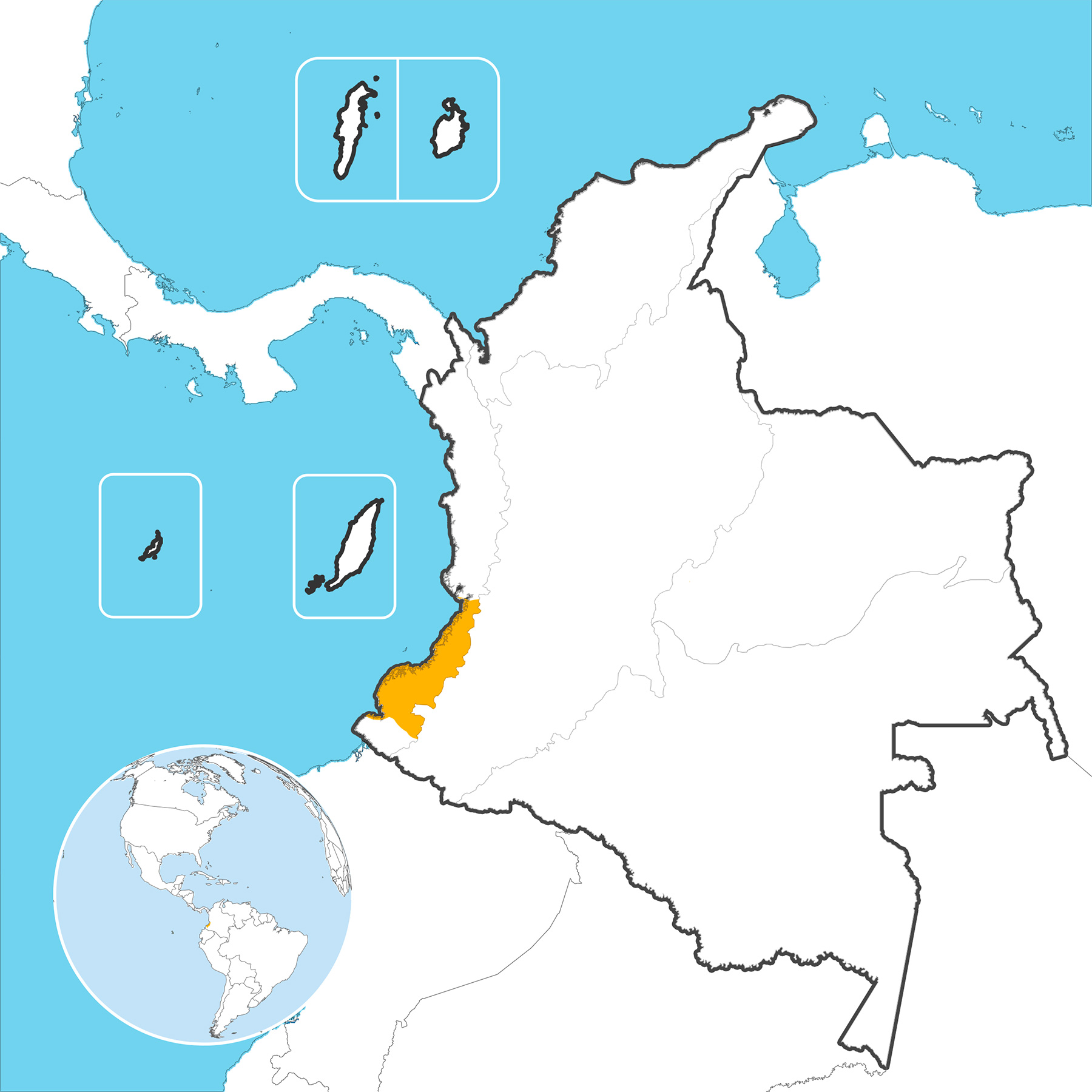
Distribution
Its geographic range is very limited, it can be found in small areas on the Colombian Pacific coast, mainly in the humid jungle of the departments of Chocó, Cauca and Valle del Cauca, its altitudinal distribution is between 50 and 200 m.
Distribution area






