
✎ Luis Mora

✎ Camilo Alméciga

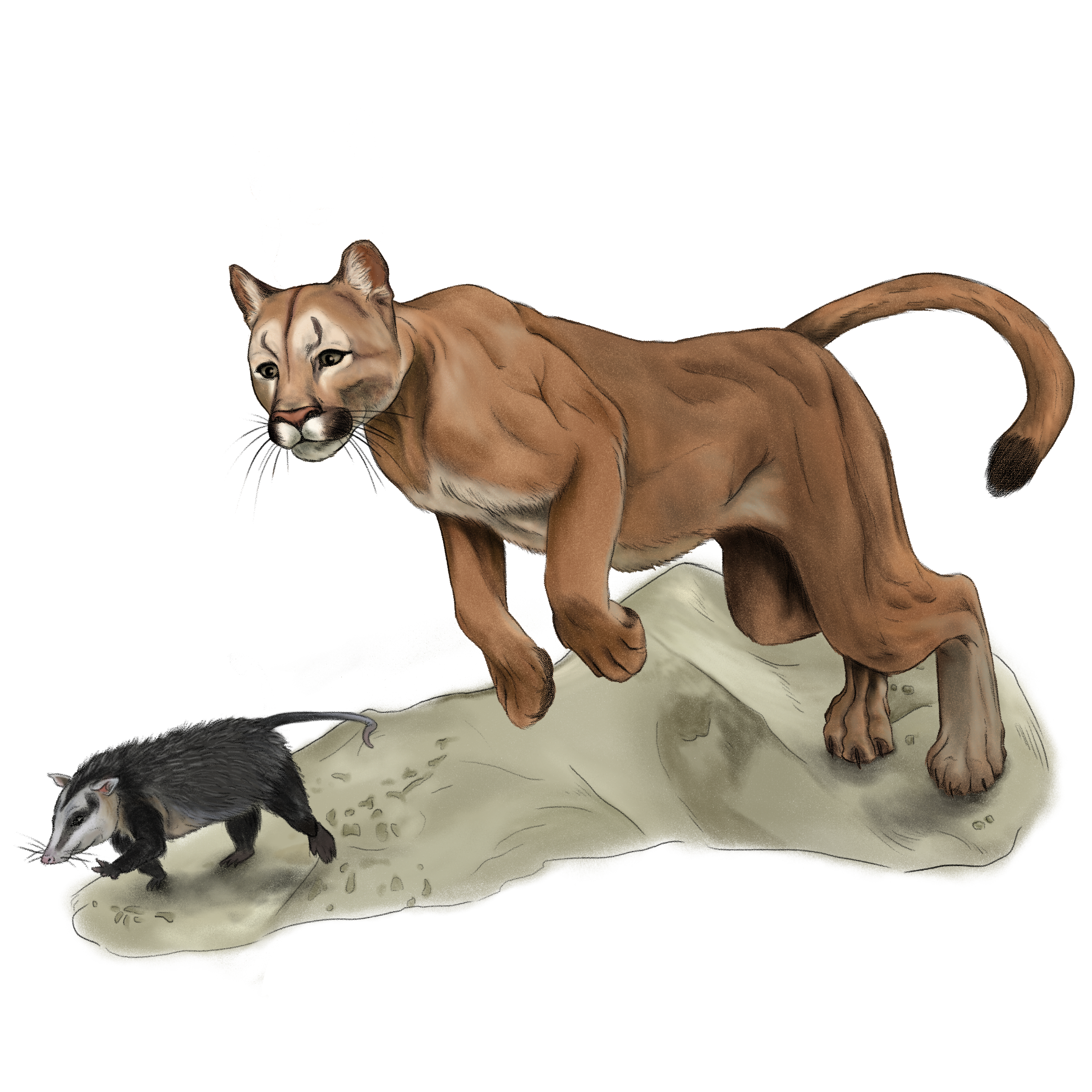
Mountain lion
Puma concolorCaribbean region
RECORRIDO VIRTUAL POR LA BIODIVERSIDAD DE COLOMBIA
Museo de Historia Natural
Universidad Nacional de Colombia

Mountain lion
Puma concolor
Morpho-functionality
Spots
Like many other kittens of other felines, these are born with spots that camouflage them very well, these spots disappear as they grow.
Senses
They make low-frequency sounds, such as chirping, purring, and howling, and mark their territory with urine.
Teeth
They have a complex of long, massive teeth specialized for cutting meat and bones. They have one molar more than the lynx and the bobcat.
Lifecycle
Males maintain territories that overlap with those of several females achieving mating this way. This can occur at any time of the year and the female's heat lasts about nine days every two months. They usually give birth every two years and the litter can have from one to six kittens; their weight at birth is between 226 and 453 g. Around day 40th they are weaned and will remain with their mother until 26 months of age. Males reach sexual maturity at around three years and females at two and a half. They have a life expectancy between 18 and 20 years.
Mountain lion
Distribution
It lives in a wide variety of habitats including the montane coniferous forests of the north of the continent, tropical lowland forests, grasslands, dry scrublands, swamps and any area with good vegetation cover and preys. They prefer shelters with dense vegetation, caves and rock crevices.
Distribution area






